|
Covert, MI and Washington, D.C., August 28, 2024--
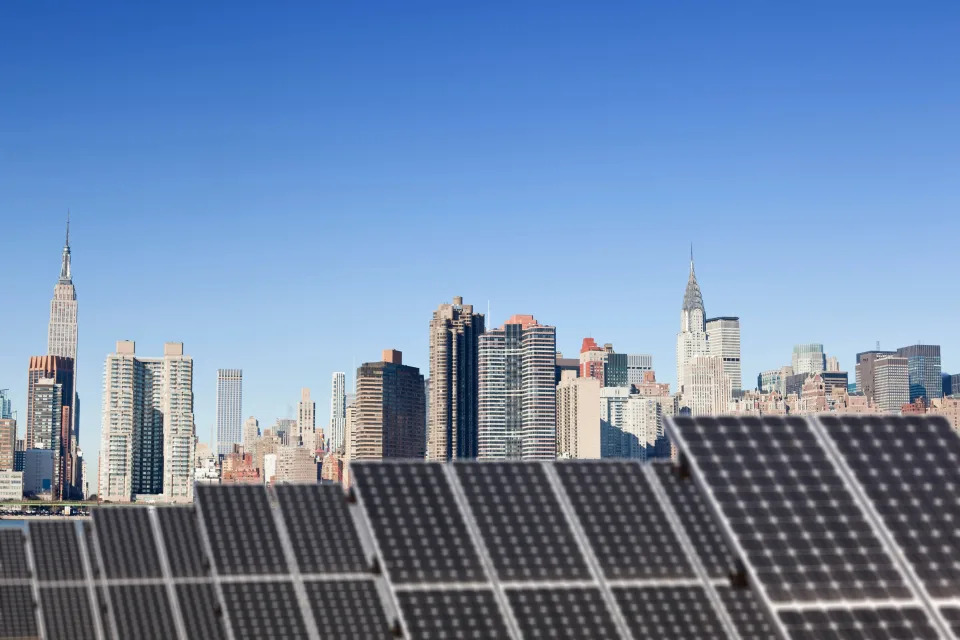
An environmental coalition, comprised of Beyond Nuclear, Don’t Waste Michigan, and Michigan Safe Energy Future, has kept up its years-long drumbeat of resistance to Holtec International’s “zombie” reactor restart scheme at the Palisades nuclear power plant. The coalition has filed an intervention petition and request for hearing on behalf of its organizations’ local members, by the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission’s (NRC) short 20-day deadline on August 27, 2024, following the related August 7, 2024 Federal Register Notice published by the agency. Most of the coalition’s legal standing declarants live within 0.75 to 1.2 miles of the atomic reactor. Palisades is located in Covert Township, Van Buren County, Michigan on the Lake Michigan shoreline.
The coalition likewise fully intends to file an intervention petition and hearing request against a so-called “Exemption” sought by Holtec, as well as several License Amendment Requests (LARs), all supposedly needed to convert Palisades’ possession-only license for decommissioning purposes, into an unprecedented, restored operating license. This deadline is October 7, 2024, 60 days after the related Federal Register Notice of August 7, 2024.
The coalition’s legal counsel, Wally Taylor of Cedar Rapids, IA, and Terry Lodge of Toledo, OH, have argued that the bait and switch trick, or con job, played by Holtec in the first place, invalidates the Entergy-to-Holtec license transfer of 2022, and prohibits the current attempt to shift the license from one Holtec holding company to another. Beginning in 2020, Holtec indicated it was seeking to take over at Palisades for decommissioning purposes only.
In February 2021, the same environmental coalition intervened against Holtec’s initial takeover, warning the controversial, scandal-ridden company could not be trusted. In addition, at that same time, Environmental Law and Policy Center, as well as the Office of the Attorney General of the State of Michigan, Dana Nessel, filed parallel interventions, arguing Palisades’ Decommissioning Trust Fund (DTF) was inadequate to carry out Holtec’s Post-Shutdown Decommissioning Activities Report plan. After meeting NRC’s short 20-day deadline, the environmental groups were kept waiting by the agency, without a word, for nearly a year and a half, only to be summarily rejected from the proceeding in July 2022. AG Nessel’s office continued to argue the DTF was $200 million short, but the proceedings were held mostly behind closed doors, supposedly to protect trade secrecy, athough the DTF has been publicly funded, by ratepayers.
But after Entergy — Palisades’ previous owner — closed Palisades for good on May 20, 2022, and then certified permanent shutdown with the NRC on June 13, 2022, Holtec wasted no time to instead pursue reactor restart. Holtec took possession of Palisades on June 28, 2022, and by July 5, 2022, had already applied to the U.S. Department of Energy for many billions of dollars of taxpayer money in order to restart Palisades. Holtec, and Michigan Governor Gretchen Whitmer, would not publicly announce the major reversal until more than two months later, on September 9, 2022. Gov. Whitmer had first floated the trial balloon for Palisades’ restart on April 20, 2022, a month before Entergy closed the reactor for good. For its part, Holtec’s CEO, Krishna Singh, had first floated the idea of building so-called “Small Modular Reactors” on the Palisades site just days earlier, in mid-April, 2022 as well.
Holtec has never operated an atomic reactor, nor has it constructed one. Holtec has proposed restarting the 57-year old (ground was broken in 1967) Palisades reactor, that operated for 51 years (from 1971 to 2022) by June 2025, and then operating the “zombie” reactor for another quarter-century, till 2051. Holtec has proposed breaking ground, also at Palisades, on two SMR-300s (300 Megawatts-electric each) by 2026, firing them up by 2030, and then operating them for many decades into the future, even though the Holtec SMR-300 design has not even been certified yet by NRC.
The coalition’s current legal intervention concludes, in part:
What emerges from Holtec’s pattern of misleads and misrepresentations respecting its acquisition of Palisades is that Holtec benefited economically while the public and the regulator are expected to absorb the economic and oversight costs of the Palisades restart to a large extent. Petitioners therefore request that the NRC revoke the original [Entergy to Holtec] December 2021 license transfer in its entirety. Moreover, Holtec owns a possession-only license for Palisades and does not have a renewed facility operating license to transfer to Palisades Energy. For that additional reason the license transfer must be denied.
Kevin Kamps from Kalamazoo, Michigan, 40 miles downwind of Palisades, who serves as radioactive waste specialist at Beyond Nuclear, stated:
“Palisades ‘zombie’ reactor restart is unprecedented, as reflected by NRC’s convoluted regulatory restart pathway that the agency and Holtec have colluded on for the past year and a half. The restart is unneeded, since renewables, storage, and efficiency can readily replace Palisades’ 800 Megawatts of electricity, as testified to by one of our coalition’s world-renowned expert witnesses, Dr. Mark Jacobson of Stanford University. The restart is insanely expensive, with Holtec requesting more than $8 billion in taxpayer and ratepayer bailouts. And it is extremely high-risk, due to long known, widespread, severe age-related degradation, as well as the lack of needed active safety maintenance since shutdown nearly two and a half years ago, and counting.”
-30- |